Gemini CLI: AI-Powered Execution of Hacking Tools on Linux Distros for Pentesting
Google’s Gemini CLI is reshaping how developers and cybersecurity professionals interact with their Linux terminals, including specialized Linux distributions designed for penetration testing. This open-source AI-powered command-line tool brings the capabilities of Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro model directly to your terminal, offering a seamless, developer-first workflow that merges natural language AI with the power of local system tools.
“Gemini CLI is a smart AI assistant you can use directly in your terminal. It’s not just for chatting, it’s purpose-built for developers.”
How Gemini CLI Works in Linux Distros for Pentesting
Linux distros tailored for penetration testing, known for their robust suite of security tools, provide an ideal environment to leverage Gemini CLI’s features. After installing Node.js (a prerequisite), Gemini CLI can be quickly set up using npm or npx commands:
sudo apt install nodejs npm
npx https://github.com/google-gemini/gemini-cli
orsudo npm install -g @google/gemini-cli
gemini
Once installed and authenticated, you simply type gemini in your terminal to start interacting with the AI.
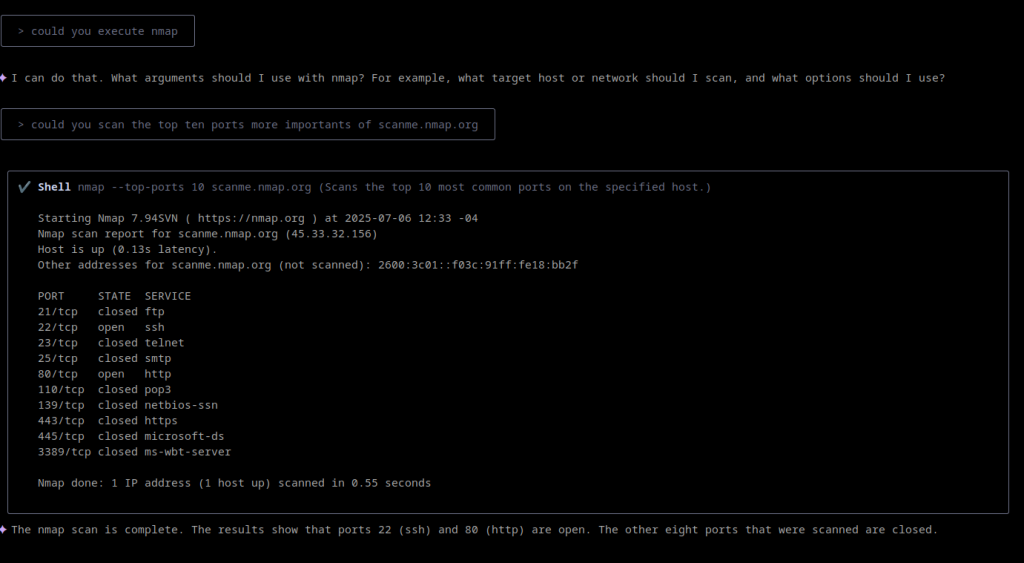
Executing Tools Like Nmap with Gemini CLI
A standout feature of Gemini CLI is its ability to reason and act within your terminal. Unlike traditional AI chatbots, Gemini CLI can interpret your natural language requests, reason through tasks, and execute commands or scripts on your system. For example, you can ask:
“Scan the local network for open ports using nmap.”
Gemini CLI will generate and execute the appropriate nmap command, then interpret and explain the results. This capability streamlines workflows for both beginners and experts, reducing the need to memorize complex command syntaxes and allowing users to focus on analysis rather than rote execution.
AI and the Future of Hacking: A Reflection
The integration of AI tools like Gemini CLI into Linux distros for pentesting signals a profound shift in both offensive and defensive cybersecurity. AI amplifies productivity, lowers barriers to entry, and accelerates both attack and defense cycles:
- For defenders, AI can automate threat detection, vulnerability analysis, and incident response, making security operations faster and more comprehensive.
- For attackers, the same AI tools can be used to automate reconnaissance, generate exploits, and evade detection, raising the sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks.
This duality introduces new ethical and practical challenges. AI’s ability to reason and act in real time blurs the line between human and machine agency in hacking. The responsibility for ethical use falls on both developers and organizations to ensure these tools are used to strengthen security rather than undermine it.
“AI-powered solutions can be used for both offensive and defensive cybersecurity purposes… To ensure that AI-powered cybersecurity solutions are used ethically and responsibly, organizations must consider the ethical implications of both offensive and defensive cybersecurity.”
Conclusion
Gemini CLI represents a new paradigm for hacking and cybersecurity: AI as a hands-on teammate in the terminal. On Linux distros for pentesting, this means you can leverage AI to run tools like nmap, automate workflows, and gain deeper insights—all from a single command line interface. As AI becomes more deeply embedded in cybersecurity, the community must balance innovation with responsibility, ensuring these powerful tools are wielded for defense, education, and the betterment of digital society.